Sichuan, China
March-April 2013
Merlion Wayfarer was recently on a trip to the mountainous regions in Sichuan, China.
The true nature of Sichuan mountains:
- Surfaces with vertical drops...
- Mountain roads with wire meshes holding the loose stones on the cliffs together to protect vehicles travelling on the roads...
- A lot of evidence of landslides - not just pebbles, but rocks too...
- Loose shale, a lot of it on the roads...
- Roads which crumble away into the valleys below...
- Valleys with fallen rocks and boulders, some changing the path of the flow of rivers...
- The most dramatic impact is a loss of habitat for millions of species. Seventy percent of Earth’s land animals and plants live in forests, and many cannot survive the deforestation that destroys their homes.
- Deforestation also drives climate change. Forest soils are moist, but without protection from sun-blocking tree cover they quickly dry out. Trees also help perpetuate the water cycle by returning water vapor back into the atmosphere. Without trees to fill these roles, many former forest lands can quickly become barren deserts.
- Removing trees deprives the forest of portions of its canopy, which blocks the sun’s rays during the day and holds in heat at night. This disruption leads to more extreme temperatures swings that can be harmful to plants and animals.
- Trees also play a critical role in absorbing the greenhouse gases that fuel global warming. Fewer forests means larger amounts of greenhouse gases entering the atmosphere - and increased speed and severity of global warming.
Sources
- "China - Places We Protect: Liangshan region, Sichuan Province". The Nature Conservancy. Retrieved from http://www.nature.org/ourinitiatives/regions/asiaandthepacific/china/placesweprotect/sichuan-province.xml (17 June 2013).
- "Deforestation". National Geographic. Retrieved from http://environment.nationalgeographic.com/environment/global-warming/deforestation-overview/ (17 June 2013).
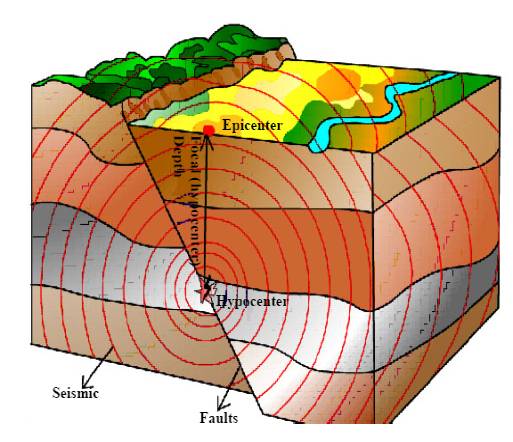
- "Longmenshan Fault". Wikipedia. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Longmen_Shan_fault (17 June 2013).
- "Managing Chinese forests responsibly" by ZHANG Kejia (23 January 2008). ChinaDialogue. Retrieved from http://www.chinadialogue.net/article/show/single/en/1650-Managing-Chinese-forests-responsibly (17 June 2013).
- "Sichuan". Wikipedia. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sichuan (17 June 2013).